Getting Started with Forex: A Step-by-Step Introduction
Getting Started with Forex: A Step-by-Step Introduction
Blog Article
Forex, short for the foreign exchange industry, could be the worldwide market place wherever currencies are traded. With an average daily trading size exceeding $6.6 trillion (BIS, 2019), it is the biggest and most fluid financial industry in the world. For anyone seeking to enter the planet of trading or grow their expense profile, knowledge the fundamentals of Forex is essential. Here, we explore the important thing blocks that may pave the best way to currency Forex Trading success.
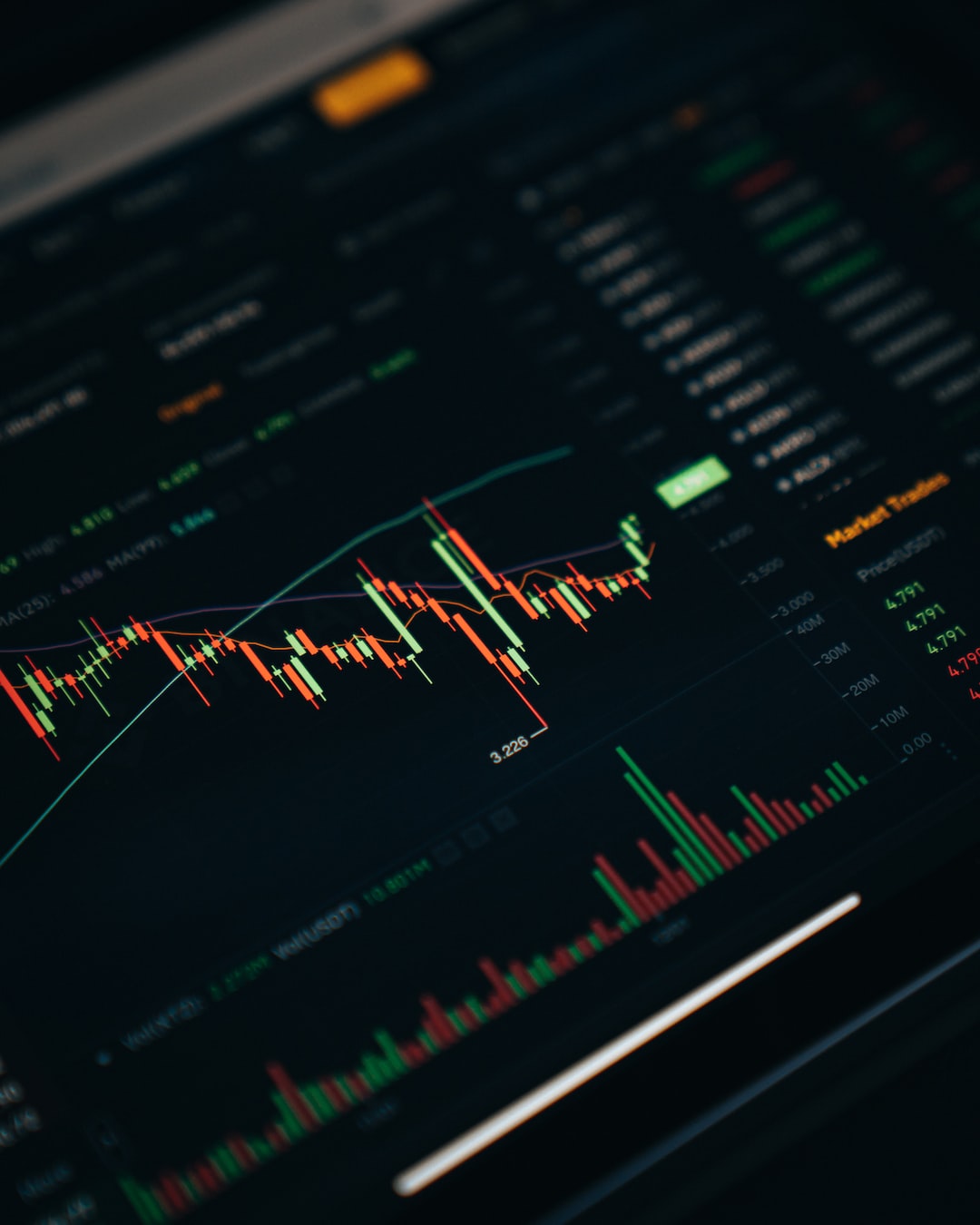
What is Forex and How Does It Work?
At its core, Forex trading involves purchasing one currency while simultaneously selling another. These trades occur in pairs—called currency pairs—such as for example EUR/USD (Euro to US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound to Japanese Yen). Currency values alter based on facets such as for example geopolitical functions, economic data, curiosity rates, and market feeling, making opportunities for traders to profit.
Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across important financial modems in cities like London, Tokyo, and New York. Unlike traditional stock exchanges, it lacks a centralized physical site, with trading conducted non-prescription (OTC). This round-the-clock supply offers equally mobility and unique challenges for traders.
Key Methods to Grasp in Forex Trading
1. Currency Sets and Pips
Knowledge currency sets is central to Forex success. Major currency pairs, just like the EUR/USD, range from the most-traded currencies internationally, while mix sets exclude the US money, and incredible couples represent emerging markets. Similarly, pips, which evaluate cost actions, help traders gauge profits and losses.
2. Leverage and Margin
Forex trading frequently requires leverage, enabling traders to control bigger amounts of income with relatively small investments. As an example, a 1:100 leverage lets a trader get a handle on $100,000 with only $1,000 of capital. However, control amplifies equally gains and risks. Margin, on another hand, is the collateral needed to start a leveraged trade.

3. Complex and Fundamental Evaluation
Successful Forex trading utilizes a mix of these strategies. Technical evaluation centers around value maps, signals, and past industry behaviors, while elementary evaluation evaluates macroeconomic factors like GDP, employment charges, and political security to outlook currency movements. Report this page